From OpenAI's groundbreaking Sora to Neuralink's futuristic brain chips, the advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) have reshaped the way we interact with technology and the world. Ever wondered why AI is evolving at such a breakneck pace? And more importantly, does this signal a future where machines outshine humans?
Before jumping to conclusions, let’s explore the foundations of AI, focusing on its two most transformative subsets: Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL).
AI in 2024: A Revolution, Not a Replacement
AI is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s part of our everyday lives. From YouTube recommendations to virtual assistants, AI influences how we learn, work, shop, and even make decisions. While some fear that machines might replace humans, the reality is different. AI isn't here to replace us but to assist, innovate, and enhance every field imaginable, including medicine, education, engineering, and entertainment.
Understanding AI, especially its core technologies like ML and DL, can feel overwhelming for beginners. But once you grasp the basics, you’ll see why learning about AI today is not just an option but a necessity.
Quick Facts: Milestones in AI History
- 1950: Alan Turing’s paper, Computer Machinery and Intelligence, introduces “The Imitation Game,” laying the groundwork for machine intelligence.
- 1955: John McCarthy coins the term "Artificial Intelligence."
- 2022: OpenAI’s ChatGPT revolutionizes conversational AI, gaining 100 million users within three months.
- 2024: OpenAI unveils Sora, hinting at AI's limitless potential.
It’s taken decades to reach this point, and while there’s more to achieve, the future of AI looks brighter than ever.
Machine Learning (ML): A Foundation of AI
What is ML?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI where algorithms enable computers to learn from data and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed. Unlike traditional programming, where humans write step-by-step instructions, ML allows machines to identify patterns, extract insights, and make data-driven decisions.
Key Applications of Machine Learning
- Image and Speech Recognition
- Facial recognition systems and virtual assistants rely on ML to identify patterns and transcribe spoken language into text.
- Recommendation Systems
- Platforms like Netflix and Amazon analyze user behavior to suggest personalized content.
- Medical Diagnosis
- ML helps healthcare professionals diagnose diseases and predict patient outcomes using data from medical records and images.
Four Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning
- Algorithms learn from labeled data to predict outcomes. Example: Spam email detection.
- Unsupervised Learning
- Works with unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns. Example: Customer segmentation in marketing.
- Semi-Supervised Learning
- Combines labeled and unlabeled data, improving accuracy while reducing the cost of data labeling.
- Reinforcement Learning
- Agents learn by interacting with an environment, receiving rewards or penalties for their actions. Example: AI-powered gaming bots.
Deep Learning (DL): Mimicking the Human Brain
Deep Learning, a subset of ML, is inspired by the human brain’s structure and function. It uses artificial neural networks to process vast amounts of data, enabling computers to perform complex tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous driving.
How Does DL Work?
- DL algorithms consist of multiple layers of interconnected neurons that process data hierarchically.
- The result? Unparalleled accuracy in tasks involving large datasets.
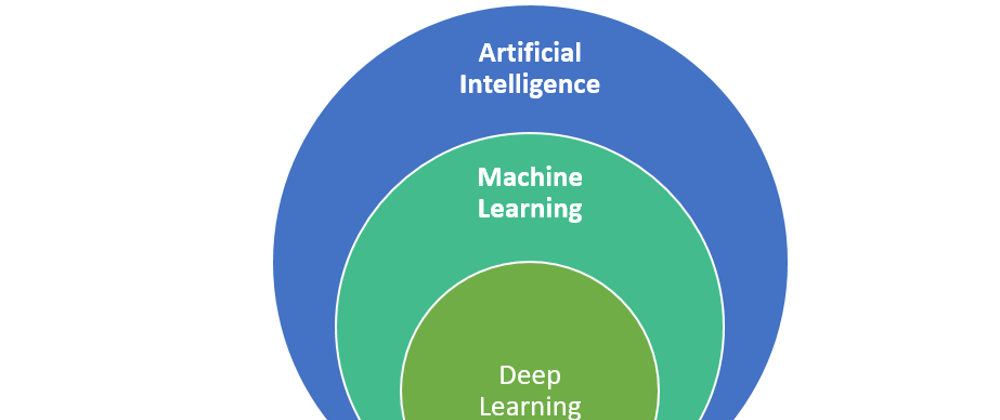
AI, ML, and DL: Understanding the Differences
- AI
- The overarching concept of machines performing tasks intelligently.
- ML
- A subset of AI focusing on learning from data to improve performance.
- DL
- A subset of ML using neural networks to solve complex problems.
Why AI Matters Today
AI has transcended science fiction to become an integral part of modern life. Whether it’s enhancing healthcare diagnostics, revolutionizing e-commerce, or powering autonomous vehicles, AI is shaping a smarter, more efficient world.
By understanding the basics of AI, ML, and DL, you’re not just keeping up with technology—you’re preparing to lead in a future where these innovations define success.
Your Journey Starts Here
AI might seem complex, but every expert was once a beginner. Whether you’re intrigued by neural networks or excited about AI applications in everyday life, this is the perfect time to dive in. Start small, stay curious, and embrace the future of technology.
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) | Deep Learning (DL) |
| AI has the ability to perform tasks, make decisions, and function as near as humans. | ML is a subset of AI. It uses complex algorithms to learn from real-world examples. | DL is a subset of M. It utilizes artificial neural networks for complex computing. |
| Can handle various tasks, from simple to complex, across domains. | It specializes in data-driven tasks like classification and regression. | Best at complex tasks such as image recognition, NLP, and more. |
| Algorithms can be simple or complex, depending on the nature of the application. | Utilizes various algorithms like decision trees, SVM, and random forests. | Relies on Deep Neural networks. Has numerous hidden layers for complex learning. |
What are the Key Components of Deep Learning?
1. Neural Networks
Neural networks are the essential building blocks of deep learning. They consist of interconnected layers of neurons, each performing simple computations. Deep neural networks can have many hidden layers, allowing them to learn complex data representations.
2. Activation Functions
Activation functions enable non-linearities in the neural network. Afterward, the network learns and models complex relationships within the data. This enables faster and more reliable training of deep neural structures. Similar activation functions such as Rectified Linear Units (ReLU) Sigmoid have applications in computer graphics and computations.
3. Backpropagation
Backpropagation is one of the fundamental algorithms used for training neural networks. It involves the repetitive adjustment of the network’s weights. Such adjustment is based on the difference between the predicted and actual output, thus minimizing the prediction error.
Applications of Deep Learning
Computer Vision The field of computer vision has rapidly advanced in a short time. Deep Learning practices enable machines to interpret and understand visual data. Major applications include image classification/segmentation and object detection. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), an artificial neural network remembers the previous input data. Such a network converts sequential input data to sequential output data. Thus, NLP is used for the Natural Language Processing tasks. Besides language translation, deep learning allows emotion analysis and text generation to be done with ease. Autonomous Vehicles One perfect example of Deep learning is Tesla’s autopilot mode, which can change lanes and suggest directions. With the help of Deep learning methods, we can develop autonomous vehicles and install sensor data, such as cameras and LiDAR.
The world of AI awaits you—are you ready to explore?

Leave a comment